Disney Stock: An Investment In A Legacy of Magic Amidst Challenges
Disney operates in three global business segments: entertainment, sports, and experiences. Entertainment and experiences benefit from franchises and characters the firm has created over a century. Entertainment includes the ABC broadcast network, several cable television networks, and the Disney+ and Hulu streaming services. Within the segment, Disney also engages in movie and television production and distribution, with content licensed to movie theaters, other content providers, or, increasingly, kept in-house for use on Disney’s own streaming platform and television networks. The sports segment houses ESPN and the ESPN+ streaming service. Experiences include Disney’s theme parks and vacation destinations, which also benefit from merchandise licensing. DIS stock is currently trading at nearly $93. Let’s have a closer look at Disney’s stock forecast.
Disney’s Earnings: Growth Trends and Future Outlook
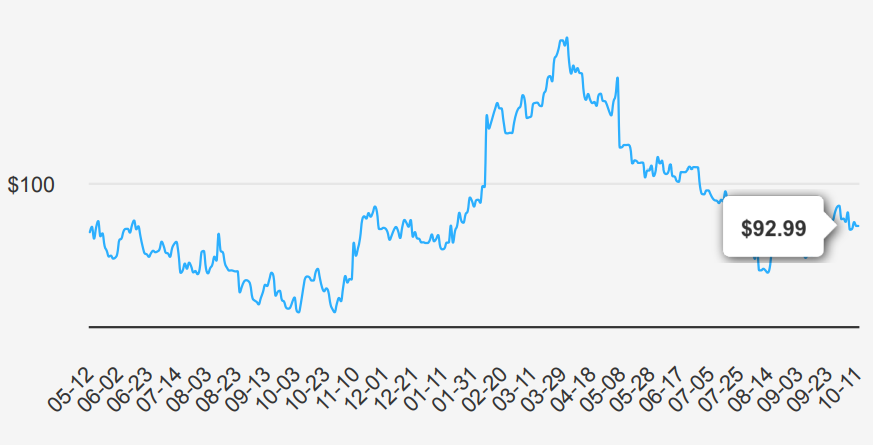
Disney’s latest quarterly results, ending June 30, 2024, showed an EPS without NRI (excludes non-recurring items) of $1.463, a notable increase from $0.874 in the previous quarter and $1.03 from the same quarter last year. This suggests significant improvements in core business operations. The EPS (Diluted) also recovered, reaching $1.43, up from -$0.01 last quarter. Revenue per share remained steady at $12.66, demonstrating resilience despite slight fluctuations. Over the past five years, annual EPS without NRI has reflected a decline at a CAGR of -17.90%, while the 10-year CAGR stands at -8.80%, indicating challenges in sustaining long-term earnings growth.
Disney’s gross margin for the quarter was 35.36%, above the 5-year median of 33.41%. This margin improvement points to cost management or pricing strategies better. However, the share buyback ratio over the past year was -2.00%, indicating a net increase in shares outstanding, potentially diluting EPS. Notably, buyback ratios are in percentage terms; thus, a -2.00% ratio means the company increased its outstanding shares by this margin. The negative ratios over recent years suggest Disney has focused on other capital allocations rather than share repurchases.
Looking ahead, analysts estimate Disney’s EPS will reach 3.504 by the end of the next fiscal year and 4.653 the following year. Revenue forecasts predict a progressive increase, with estimates at $91,241.81 million for 2024, climbing to $99,192.34 million by 2026. These projections indicate cautious optimism for growth, likely driven by strategic initiatives and market expansions. The next earnings release is on November 14, 2024, providing further insights into Disney’s stock forecast and strategic direction.
Disney Stock’s Economic Value Creation Challenges
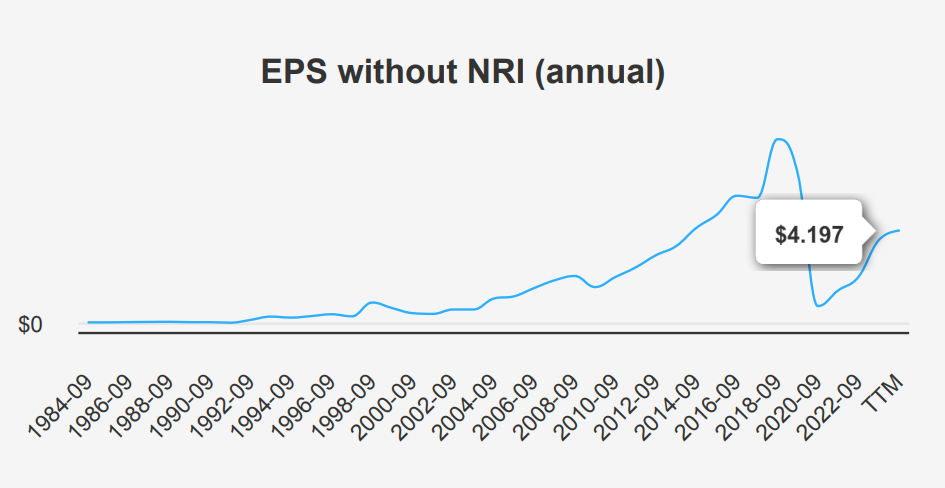
Disney stock forecast and fundamental performance can be assessed through its Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) relative to its Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC). A comparison of these metrics indicates whether the company is generating economic value. The company’s current ROIC stands at 4.72%, which is below its current WACC of 9.99%. This suggests that Disney is currently not generating positive economic value, as it is earning less on its invested capital than the cost of that capital.
Over the past five years, Disney’s median ROIC was 2.99%, again lower than the median WACC of 7.87%. This historical perspective reinforces the current trend of underperformance in terms of value creation. The high variability in these figures, with a 10-year ROIC high of 14.56% and a low of 2.03%, indicates fluctuating efficiency in capital utilization. Despite past instances of higher ROE peaks, sustained performance above WACC is crucial for long-term value creation, and Disney needs to focus on improving its ROIC to exceed its WACC consistently.
Disney’s Dividend Strategy: Stability Amidst Financial Challenges
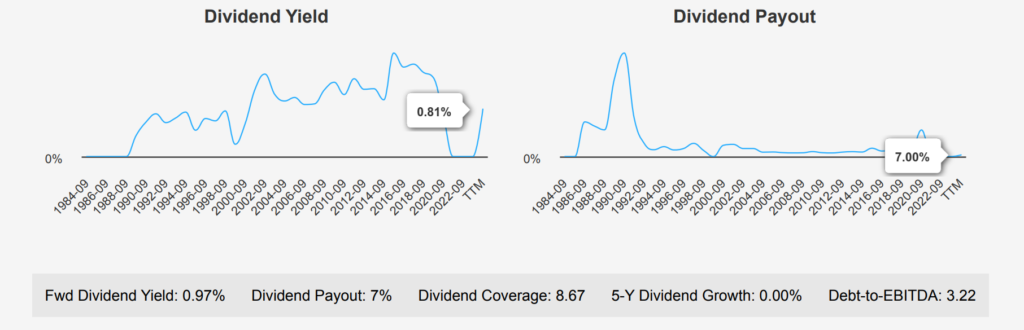
Disney has maintained a dividend payout ratio of 7.0%, significantly lower than its historical highs and lows, indicating a conservative approach to dividend distribution. Disney’s current forward dividend yield stands at 0.97%, which is modest against its 10-year median yield of 1.38%.
The company’s Debt-to-EBITDA ratio is 3.22, placing it in the moderate risk category. Although this level is manageable, it suggests that Disney should be cautious with additional debt to maintain financial flexibility, especially in light of its stagnant dividend growth.
Given the dividend frequency of twice a year, the next ex-dividend date after July 8, 2024, might be on January 8, 2025.
Unlocking Disney’s Hidden Value: A Deep Dive
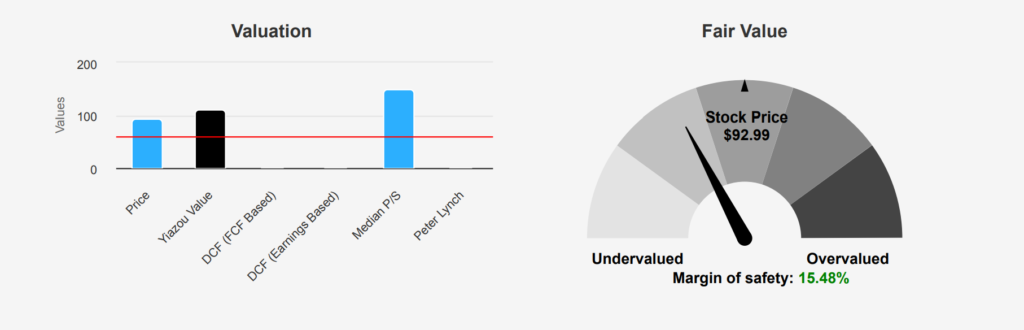
Disney’s current intrinsic value stands at $110.02, compared to its market price of $92.99, presenting a margin of safety of 15.48%. This suggests that the stock is undervalued, offering investors a potential buffer. Under Disney stock forecast, the Forward P/E ratio at 17.99, it is below its TTM P/E of 35.77, indicating expectations of earnings growth. Historically, the P/E has been volatile, with a 10-year high of 301.84 and a median of 21.78, suggesting the current valuation is relatively reasonable compared to past highs but slightly above the median.
The TTM EV/EBITDA ratio is 14.3, aligning closely with its 10-year median of 14.75 and well within its historical range. This indicates the company is priced fairly relative to its earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. The TTM Price-to-Free-Cash-Flow ratio of 21.43 is lower than its 10-year median of 27.26, suggesting an attractive valuation based on cash flow generation. Additionally, the TTM Price-to-Book ratio is 1.68, below the 10-year median of 3.37, highlighting a potential undervaluation based on asset value.
Analyst ratings reflect a stable outlook for Disney, with a price target of approximately $111.22, consistent over the past weeks. While there is a slight decrease from two months ago, the target remains above the current price, supporting the view of undervaluation. Overall, the metrics suggest Disney is currently trading below its intrinsic value, with several indicators pointing towards a favorable valuation compared to historical norms, offering a potential investment opportunity with a reasonable margin of safety
Navigating the Risks and Rewards of Disney’s Future
The company faces several financial challenges that could impact Disney stock forecast. A notable concern is the company’s asset growth rate of 10.9%, which significantly outpaces its revenue growth rate of 3.8% over the past five years. This suggests potential inefficiencies in asset utilization. Additionally, both the gross margin and operating margin have been declining, with average annual decreases of 5.3% and 17.6%, respectively. These trends indicate that Disney is facing cost management issues. Moreover, the company’s return on invested capital (ROIC) is lower than its weighted average cost of capital (WACC), hinting at capital inefficiency. The Altman Z-score of 2.01 places Disney in the “grey area,” suggesting some level of financial stress.
Conversely, there are positive indicators for Disney’s financial health. The Piotroski F-Score of 8 is robust, signaling strong financial performance. Insider buying within the last three months, with 11,756 shares purchased, reflects confidence from those within the company. The Beneish M-Score of -2.67 suggests a low risk of earnings manipulation. Additionally, the stock’s price-to-earnings (PE) ratio is near its three-year low, and the dividend yield is approaching a three-year high, potentially attracting value-focused investors. These factors may provide a buffer against the risks over Disney stock forecast, but ongoing monitoring is recommended.
Disney Insider Activity: A Cautious Optimism Unveiled
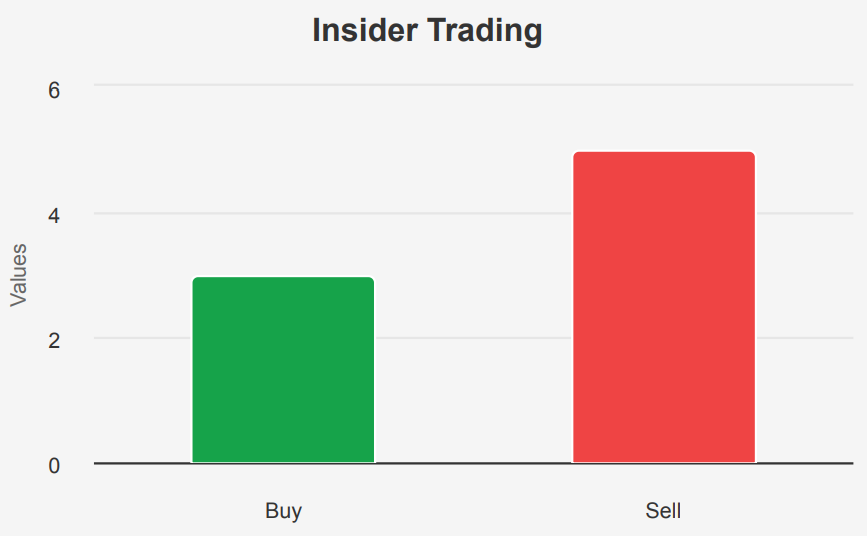
An analysis of insider trading trends for Disney over the past year reveals a cautious yet intriguing pattern. Over the past six months, two insider purchases were against one sale, suggesting a period of mixed sentiment but leaning toward optimism. However, examining the full 12-month period, insiders made three purchases and five sales, reflecting a more balanced yet slightly risk-averse stance.
Insider ownership remains relatively low at 0.97%, which might indicate limited influence by internal stakeholders on strategic decisions. On the other hand, institutional ownership is significantly higher at 68.35%, suggesting that institutional investors strongly influence the company’s stock performance and strategic directions.
Overall, the trend suggests that while there is some insider confidence, the relatively low insider ownership and higher institutional control might mean major insiders are cautious, potentially reflecting broader market conditions or company-specific challenges.
Disney Stock’s Liquidity
Disney exhibits moderate liquidity and trading activity. The current daily trading volume stands at 6,293,524 shares, which is below the two-month average daily trading volume of 8,945,816 shares. This indicates a recent decrease in trading activity, suggesting potential investor caution or market volatility impacting Disney’s stock.
The Dark Pool Index (DPI) is at 21.98%, reflecting the proportion of trades occurring in dark pools. A DPI of 21.98% suggests that a significant portion of trading activity is happening off-exchange, potentially indicating institutional investor interest and the strategic accumulation or distribution of shares.
The lower-than-average trading volume combined with a notable DPI may imply that while general market interest has dipped, institutional players remain active. Overall, while Disney maintains a significant presence in the market, the current trading dynamics suggest a cautious environment, with institutional trades potentially driving price movements more than retail activity.
Congress Members’ Strategic Moves in Disney Stock
In recent months, two significant trades involving shares of DIS stock have been reported by members of Congress. On September 4, 2024, Representative John James, a Republican from the House of Representatives, sold between $1,001 and $15,000 worth of Disney stock. The trade was reported on September 6, 2024, and last modified on September 9, 2024. Not long before, on July 25, 2024, Senator Sheldon Whitehouse, a Democrat, executed a full sale of Disney shares within the same value range. This transaction was reported on August 21, 2024, and last modified on the same day. Both sales occurring close together may suggest a cautious stance among lawmakers towards the entertainment giant amidst potential market volatility or company-specific challenges. These trades highlight a bipartisan movement away from Disney, which could reflect broader market sentiments or personal portfolio strategies.
Disclosures:
Yiannis Zourmpanos has a beneficial long position in the shares of DIS either through stock ownership, options, or other derivatives. This report has been generated by our stock research platform, Yiazou IQ, and is for educational purposes only. It does not constitute financial advice or recommendations.






