Intel Stock’s Edge In Expanding Role Beyond Microprocessors: A Strategic Pivot
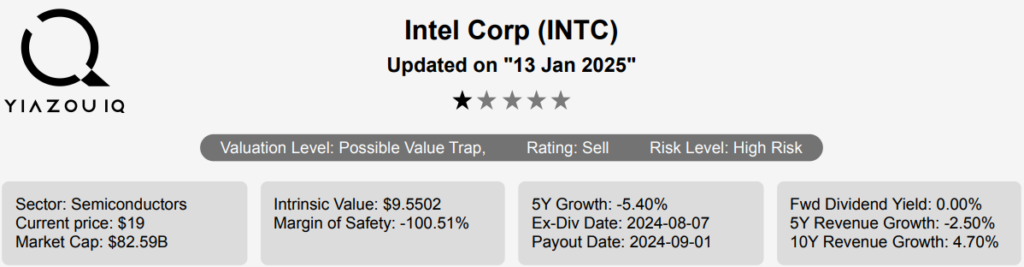
Intel is a leading digital chipmaker, focused on the design and manufacturing of microprocessors for the global personal computer and data center markets. The company pioneered the x86 architecture for microprocessors and was the prime proponent of Moore’s law for advances in semiconductor manufacturing. Intel remains the market share leader in central processing units in both the PC and server end markets. It has also been expanding into new adjacencies, such as communications infrastructure, automotive, and the Internet of Things. Further, Intel expects to leverage its chip manufacturing capabilities into an outsourced foundry model where it constructs chips for others. Intel stock is currently priced at ~$19.15. Let’s explore INTC stock forecast.
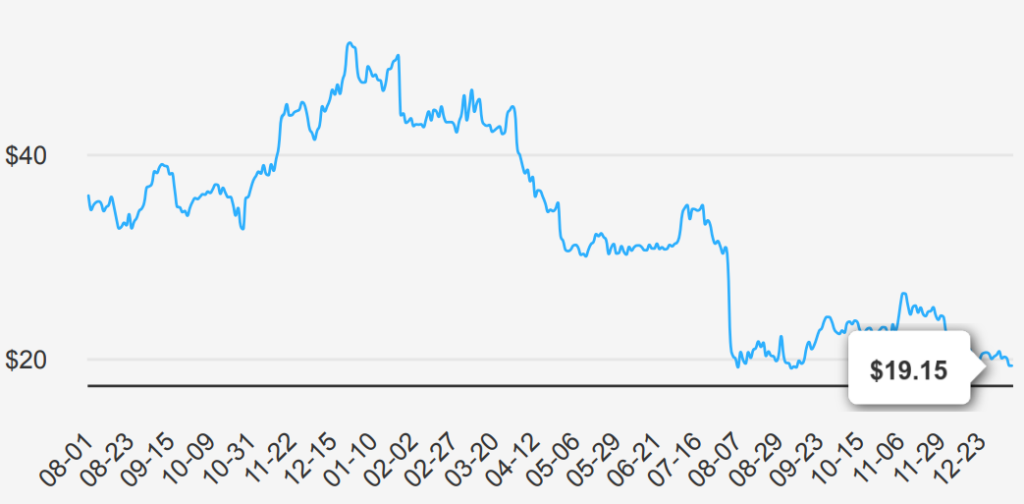
Intel EPS Decline and Revenue Challenges Through 2025
INTC reported a challenging Q3 2024, with EPS without NRI (excluding non-recurring items) at -$0.46, a sharp decline from $0.02 in Q2 2024, and $0.41 in Q3 2023, highlighting substantial year-over-year and quarter-over-quarter setbacks. Revenue per share for Q3 2024 was $3.095, slightly up from Q2 2024’s $3.007 but down from $3.348 in Q3 2023. The company’s EPS without NRI has shown a 5-year Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of -26.10% and a 10-year CAGR of -0.20%, aligning with the broader industry’s headwinds projected at 4.5% growth over the next decade, reflecting significant challenges ahead under INTC stock forecast.
Intel’s gross margin fell to 34.67%, the lowest in the past decade, compared to a 5-year median of 55.45% and a 10-year median of 59.79%, demonstrating considerable pressure on profitability. The share buyback ratio over the past year was -2.20%, indicating an increase in outstanding shares rather than a reduction, compared to a 5-year buyback ratio of 1.20%, suggesting limited recent buyback activity. A negative buyback ratio means more shares were issued than repurchased, potentially diluting EPS further. The lack of significant share repurchase activity has not provided the typical EPS enhancement seen in other periods.
Looking ahead, Intel faces significant hurdles, with analysts estimating a negative EPS of -$4.346 for FY1 ending 2025 and -$0.060 for FY2 ending 2026. Revenue may grow from $52.67 billion in 2024 to $59.9 billion by 2026, suggesting some recovery. However, with an upcoming earnings date set for January 24, 2025, Intel will need to address these challenges to reassure investors and realign with market growth expectations.
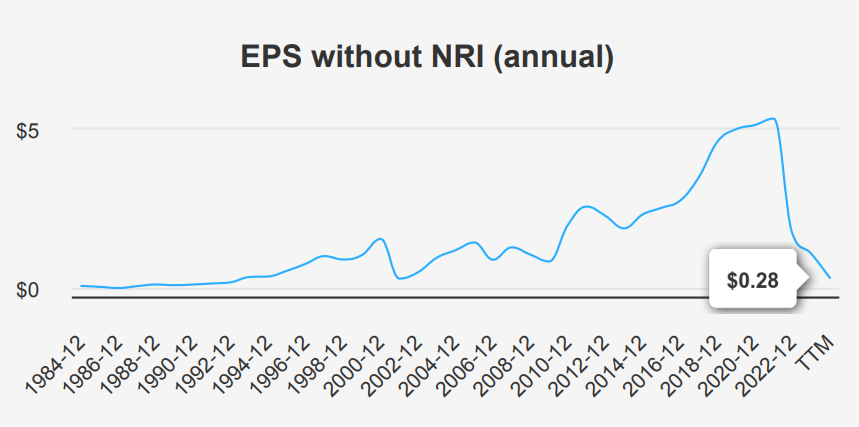
Intel’s ROIC Plunges Below WACC: A Reversal in Economic Value Creation
INTC Stock has historically demonstrated a strong ability to create economic value, as indicated by its 5-year median Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) of 16.74%, significantly surpassing the Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) of 5.66%. This suggests that over the past five years, Intel has been generating returns well above its cost of capital, thereby creating shareholder value.
However, a closer look at the most recent figures reveals a concerning shift. The current ROIC stands at -4.27%, which is substantially below the current WACC of 9.62%. This indicates that Intel is currently not covering its cost of capital, leading to a destruction of economic value. This negative trend is further corroborated by the current Return on Equity (ROE) of -15.11%, compared to a 10-year high of 29.33%.
Historically, Intel’s ROIC has been as high as 20.11%, showing its potential for value creation. To return to such levels, the company must enhance operational efficiency and strategic investments to realign its ROIC above the WACC, thereby restoring positive economic value creation. This decline in financial efficiency suggests potential issues in capital allocation or operational challenges that Intel needs to address to restore its value-creation capabilities.
Intel Stock’s Unsustainable Dividend Strategy and High Payout Risk
INTC has exhibited a significant decline in its dividend growth, with a 5-year dividend growth rate of -5.40% and a more pronounced 3-year rate of -17.50%. The company’s forward dividend yield is currently indicating that future dividend payments are uncertain. The high dividend payout ratio of 179.0% suggests that Intel is paying out more in dividends than it earns, which is unsustainable over the long term.
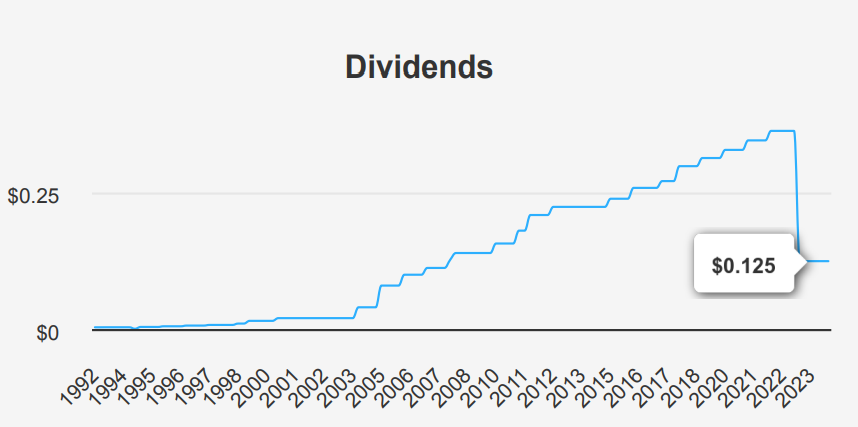
Comparatively, Intel’s Debt-to-EBITDA ratio stands at 15.27, well above the industry guideline of 4.0, indicating high financial leverage and potential risk in meeting its debt obligations. This financial strain is likely contributing to Intel’s negative forecasted 3- 5 year dividend growth rate of -55.20%. In the broader sector context, Intel’s dividend yield has historically fluctuated, but current trends suggest a move away from regular dividends, reflecting the company’s need to manage its financial position more prudently.
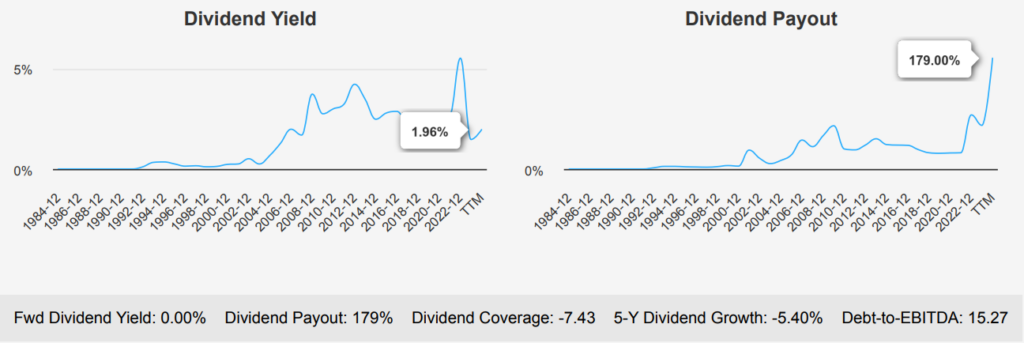
Intel Stock Overvaluation: Intrinsic Value vs. Market Price
Intel’s current market price of $19.15 significantly exceeds its intrinsic value of $9.55, suggesting a negative margin of safety of -100.52%. This indicates that the stock is currently overvalued when compared to its intrinsic value, presenting a potential risk for investors seeking undervalued opportunities. The Forward P/E ratio stands at 19.62, which, while not at the historical high of 149.96, exceeds the 10-year median of 13.43, hinting at a premium pricing relative to historical norms.
The TTM Price-to-Sales (P/S) ratio is 1.51, near its 10-year low of 1.46, suggesting the stock is trading at a relatively lower revenue multiple. However, the TTM EV/EBITDA is notably high at 34.66, far above the 10-year median of 7.29, indicating potential overvaluation based on earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. The TTM Price-to-Book (P/B) ratio is 0.83, close to the 10-year low of 0.70, reflecting a reasonable valuation against its book value.
Despite these valuation metrics, analyst ratings and price targets suggest a cautious optimism, with a current price target of $24.82, slightly down from previous months. This reflects some uncertainty or transitional sentiment in the market about Intel’s near-term prospects. Overall, while certain metrics like P/B ratio appear attractive, the high EV/EBITDA and negative margin of safety point towards a cautiously overvalued position, requiring careful consideration from investors under INTC stock forecast.
Assessing Intel’s Financial Risks and Limited Rewards
INTC faces several financial challenges that could impact its stock performance and overall stability. The company has consistently issued new debt, totaling USD 10.8 billion over the past three years, which raises concerns about its leverage and long-term financial health. With a Piotroski F-Score of 3, Intel’s business operations appear to be underperforming, and its Altman Z-score of 1.13 places it in the distress zone, indicating a potential risk of bankruptcy within two years. The company’s gross and operating margins have been declining sharply, with operating margins dropping at an average annual rate of 66.2% over the past five years.
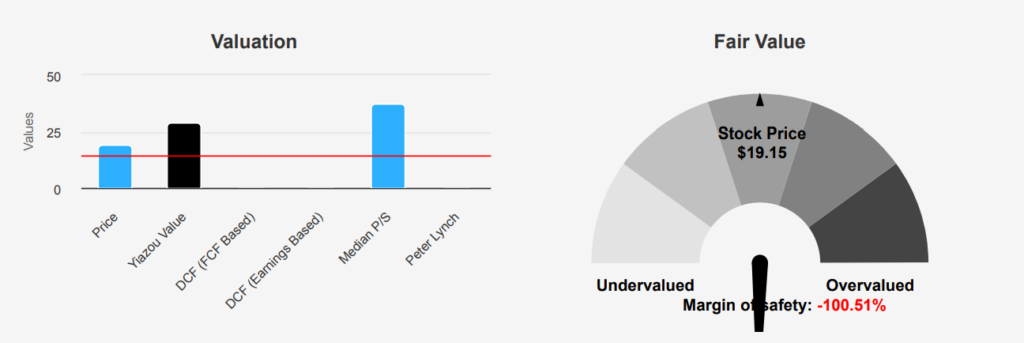
Additionally, its dividend payout ratio of 1.79 suggests that the current dividend levels may not be sustainable. Despite these challenges, there are some positive indicators worth noting. Recent insider buying, totaling 11,150 shares, suggests some confidence from within the company. Furthermore, the stock price is near its 10-year low, offering potential value for investors willing to take on risk. The price-to-sales ratio is also close to its 10-year low, which may attract value-focused investors. However, given the financial warning signs, any investment in Intel should be approached with caution, considering both the potential for recovery and the significant risks involved in INTC stock forecast.
Intel Insiders Show Modest Optimism Amid Low Ownership Levels
Over the past year, insider trading activity at INTC has shown a modestly positive trend. In the last 12 months, there have been six insider buys compared to just one insider sell, indicating potential confidence from the company’s directors and management in the company’s future prospects. This trend is consistent over the medium term, with two buys and one sell in the past six months, and one buy and one sell in the last three months.
The consistent buying pattern suggests that insiders may believe the stock is undervalued or that the company has growth potential. However, the relatively low insider ownership at 0.52% indicates that insiders do not hold a significant stake in the company, which might limit the impact of their trading activity on stock perception.
Institutional ownership stands high at 68.23%, suggesting strong institutional interest and possibly a stabilizing influence on the stock’s volatility. The balance of insider activity and institutional support may reflect a cautiously optimistic outlook for Intel’s performance and INTC stock forecast.
Intel’s Liquidity: High Activity with Recent Volume Dip
INTC stock exhibits significant liquidity and trading activity, reflected in its average daily trading volume of 69,796,354 shares over the past two months. This level of volume suggests robust investor interest and facilitates ease of entry and exit for traders in the market. The recent daily trade volume of 69,579,747 shares aligns closely with the two-month average, indicating consistent trading patterns. This stability in volume suggests a balanced flow of buying and selling activity, which can contribute to maintaining orderly market conditions.
The Dark Pool Index (DPI) for INTC stands at 56.14%, highlighting that a substantial portion of trades occur in private venues rather than on public exchanges. A DPI above 50% often indicates significant institutional activity, as institutions frequently use dark pools to execute large orders without causing price disruption. Overall, INTC’s trading metrics reveal a liquid stock with high trading volumes and notable institutional participation through dark pools. Under INTC stock forecast, these factors combine to make INTC an attractive option for investors seeking a stock with ample liquidity and active trading dynamics.
Intel’s Declining Patent Filings: 37% Drop Since 2019
INTC displayed a fluctuating yet generally declining trend in U.S. patent filings from 2019 to 2024. In 2019, Intel secured 3,056 patents, the highest in the given period. This number decreased notably to 2,427 in 2020, slightly rebounded to 2,630 in 2021, and then continued its downward trajectory to 2,418 in 2022. By 2023, patents further dropped to 2,146, and the trend persisted into 2024 with a low of 1,923 patents, illustrating a strategic shift or reduced R&D output.
Diverging Opinions on Intel Stock by U.S. Representatives
In November 2024, two notable trades were reported involving Intel Corporation (INTC) by members of the U.S. House of Representatives. On November 1, Marjorie Taylor Greene, a Republican representative, made a purchase valued between $1,001 and $15,000. Just a week later, on November 8, Mike Kelly, also a Republican, executed a sale of Intel stock within the same financial range.
These trades are interesting as they occurred close to each other, suggesting differing market perspectives or personal financial strategies among the representatives. Greene’s purchase indicates a potential belief in the future growth or stability of Intel, while Kelly’s sale could suggest a decision to capitalize on current stock prices or divest for portfolio rebalancing. Such transactions underscore the diverse approaches legislators might take in managing their personal investments, even within the same party.
Disclosures:
On the date of publication, Yiannis Zourmpanos did not hold (either directly or indirectly) any positions in the securities mentioned in this article. This report has been generated by our stock research platform, Yiazou IQ, and is for educational purposes only. It does not constitute financial advice or recommendations.






