Super Micro Computer, Inc. (SMCI) is a major server and storage solutions company that operates in various segments, including enterprise data centers, cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), 5G, and edge computing. SMCI offers services that cover complete servers, storage systems, modular blade servers, blades, workstations, full-rack scale solutions, networking devices, server subsystems, server management, and security software. The company operates globally to help customers install, upgrade, and maintain computing infrastructure. SMCI’s offerings ensure a high degree of flexibility and customization through several server models and configurations tailored to customers’ computing needs. The company posted annual sales of $15 billion during FY24 (year-over-year growth of 109.8%) and forecasts a revenue of $26-30 billion for FY25 and a dominant market share of ~23.0% in the AI server market, critical components of our SMCI stock forecast.
Early Years (1993-2000)
Super Micro Computer was established in 1993. In the early years, the company developed high-powered computer servers in San Jose, California. Soon, the company started to provide customizable solutions apart from off-the-shelf offerings. Meanwhile, the company initially served original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), but soon, they added enterprise-level customers as the custom server market expanded. SMCI emphasized research and development in the early years, which enabled them to spearhead innovation rapidly in the growing and ever-changing hardware industry, and it allowed them to expand into different markets within the server and storage system whenever opportunities arose.
Expansion and Product Diversification (2000-2010)
SMCI expanded rapidly in the early 2000s, introducing complete server systems and storage solutions along with barebone systems, and transformed the company into an end-to-end IT solutions provider. The company became a major player in the enterprise IT and data center markets, offering customizable and energy-efficient products. SMCI’s cost-effective solutions stood out among the competitors (e.g., Dell, HP). The company became a preferred supplier among data centers and cloud providers. As the company’s growth accelerated, it expanded its global presence with manufacturing facilities in the United States, Taiwan, and the Netherlands.
Innovation and Technological Leadership (2010-Present)
As the demand for complex computing increased, particularly in cloud computing, big data, and AI, SMCI broadened its product portfolio to tap into the opportunity. In 2014, the company launched liquid cooling technology for its servers, which improved performance while lowering energy usage. This breakthrough was especially crucial given the increased need for AI and machine learning workloads, which required energy-intensive computer power. The company’s relentless effort to provide cost-efficient solutions made it a leading player in the industry. SMCI also became the first few companies to introduce green computing solutions. SMCI went public in 2007 to raise $64 million for further expansion. The company started funding projects to develop products for cloud computing and enterprise applications.
Expansion into Artificial Intelligence and Emerging Technologies (2020-Present)
SMCI has intensified its focus on the buoyant AI and machine learning businesses. The company has expanded its product offerings to AI researchers, data analysts, and cloud providers. It has also expanded into edge computing, targeting industries such as 5G, driverless vehicles, and the Internet of Things (IoT), which require customized computing infrastructure. The company now has ~ a 23.0% share in the AI server market.
Leadership and Ownership Structure
SMCI is a founder-led company. Charles Liang, the CEO and co-founder of Supermicro, has remained in the leadership role since its inception. The ownership structure of the company is as follows:
| Shareholder Name | Shares Owned | Ownership Percentage |
| Charles Liang | 67,403,640 | 11.51% |
| Vanguard Fiduciary Trust Co. | 61,474,200 | 10.50% |
| BlackRock Advisors LLC | 33,730,990 | 5.76% |
| State Street Corporation | 21,381,420 | 3.65% |
| Yih-Shyan Liaw | 15,423,365 | 2.63% |
Source: Market Screener
Super Micro’s Business Model
SMCI designs, manufactures, and sells various server and storage systems. The company’s product portfolio includes:
- Barebone Systems: Partially assembled systems allow customers to customize hardware configurations to meet specific requirements.
- Complete Systems: Fully integrated server systems optimized for various applications, such as cloud computing, big data, and enterprise workloads.
- Modular Server Subsystems and Accessories: These include components such as server boards, chassis, power supplies, and other accessories that enable flexible and scalable solutions.
SMCI’s building block architecture allows for rapid customization and tailoring services based on customers’ needs. This approach has been particularly advantageous in the AI sector, where the company has developed proprietary liquid cooling systems to meet the high-performance demands of AI workloads.
SMCI’s revenue comes mostly from selling server and storage systems, accounting for approximately 94.7% of total revenue during FY24. The company designs the systems for various applications, including data centers and high-performance computing environments. Subsystems and accessories contribute about 5.3% to the overall revenue. These products support the main server offerings and cater to customer customization needs. Considering the vertical markets, OEM Appliance & Large DC contributes 57.9%, Organic (Enterprise & Channel) contributes 40.6%, and 5G, Telco & Edge/IOT contributes 1.5% to the total revenue.
SMCI has been on a high growth trajectory driven by its server and storage market dominance. Superior innovation and fast-moving approach to providing low-cost solutions to complex computing needs have propelled the company to the top position in the market. As the company grew its scale rapidly, profitability also expanded sharply. The company’s revenue posted a CAGR (Compounded Annual Growth Rate) of 33.7% during FY19-24 and operating profit registered a CAGR of 67.1% in the same period. The company’s operating margin improved by 573 basis points to 8.5% over the last five years.
Supply Chain
Supermicro’s supply chain encompasses several key components, including materials sourcing, manufacturing processes, distribution, and customer engagement. This structure enables the company to efficiently produce and deliver customized server solutions while maintaining competitive pricing and quality.
Sourcing Materials
Supplier Relationships
Supermicro relies on a network of suppliers for critical components such as motherboards, chassis, and other electronic parts. For example, Ablecom and Compuware are two key suppliers that provide essential elements for Supermicro’s products.
Procurement Strategy
The procurement strategy involves:
- Global Sourcing: SMCI sources materials from various international suppliers to mitigate risks associated with local supply disruptions.
- Cost Management: The company aims to maintain cost efficiency by leveraging its relationships with family-owned suppliers, although this approach may limit competitive pricing opportunities compared to independent suppliers
Manufacturing Processes
In-House Manufacturing
Supermicro has manufacturing facilities in Silicon Valley, Taiwan, and the Netherlands, where it assembles servers and storage systems. The manufacturing process includes:
- Modular Design: This allows for flexibility in production, enabling the company to adapt to customer specifications and market demands.
- Quality Control: Despite challenges reported regarding product quality and assembly standards, Supermicro emphasizes rigorous testing protocols during manufacturing to ensure reliability
Outsourced Manufacturing
In addition to in-house production, Supermicro collaborates with contract manufacturers for certain components. This approach helps manage production costs while scaling operations based on demand fluctuations.
Distribution Network
Supermicro employs a multi-tier distribution model that includes:
- Direct Sales: Selling directly to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and large enterprise customers.
- Distributors: Partnering with distributors such as Avnet and Tech Data allows Supermicro to reach a broader market without the overhead of maintaining a large sales force.
Customer Engagement
Supermicro provides customized server solutions tailored to meet specific customer needs across various industries, including cloud computing, AI, and enterprise IT. This approach enhances customer satisfaction and fosters long-term relationships. The company offers extensive support services post-sale, ensuring customers receive assistance with installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. This commitment helps build brand loyalty and encourages repeat business.
SMCI in AI Supply Chain:
SMCI is a major player in the AI revolution. In the AI supply chain, SMCI plays a crucial role by providing customized servers and storage systems to meet the requirements of AI workloads. Leveraging its modular building block architecture, SMCI offers customizable, scalable hardware configurations that cater to industries requiring high-performance computing, such as cloud computing, autonomous vehicles, and IoT. Its proprietary liquid cooling technology further enhances its position by improving energy efficiency—a critical factor for the energy-intensive AI and machine learning sectors.
With a 23% market share in the AI server market, SMCI supplies major cloud providers, AI researchers, and enterprises, offering green computing solutions that align with growing sustainability priorities. Its global manufacturing capabilities, spanning the U.S., Taiwan, and the Netherlands, allow the company to scale production to meet surging demand while maintaining cost efficiency. These factors have made SMCI a leader in the rapidly growing AI infrastructure space, enabling organizations to deploy cutting-edge workloads effectively.
However, challenges persist. SMCI relies heavily on key suppliers like Ablecom and Compuware for critical components, exposing the company to supply chain risks and limiting cost optimization opportunities. The AI server market is fiercely competitive, with industry giants like NVIDIA and AMD advancing their offerings and pressuring SMCI to maintain its technological edge. Governance concerns stemming from delayed financial reporting further strain investor confidence, creating potential headwinds for sustained growth. Despite these challenges, the increasing demand for AI infrastructure presents significant opportunities. By expanding its product offerings in emerging fields like edge computing and 5G, while continuing to invest in AI-optimized hardware, SMCI is well-positioned to maintain its leadership. Its ability to innovate rapidly and deliver cost-effective, energy-efficient solutions will remain critical in capturing a growing share of the AI supply chain and driving future growth in the sector.
Source: Semiwiki
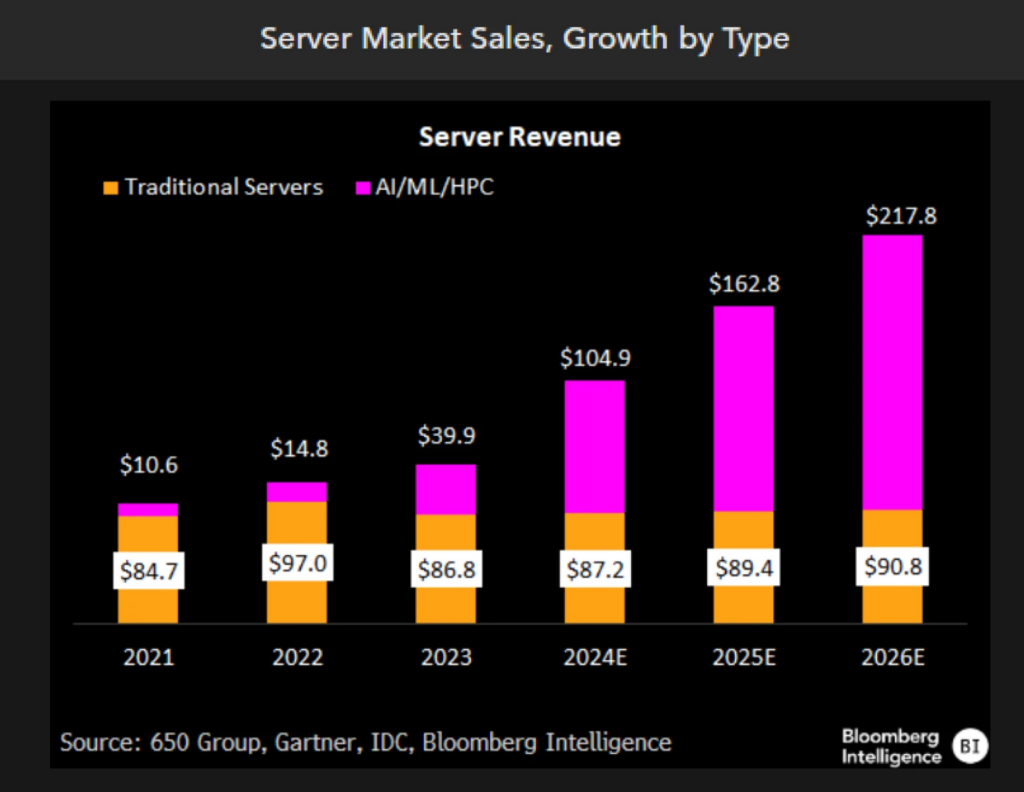
AI Server Boom: The $252 Billion Race Reshaping Tech Giants
The AI server market is poised for rapid expansion, with projected growth of 55% in 2025, reaching $252 billion. This surge is driven by the increasing adoption of AI across hyperscale cloud providers, enterprise customers, and tier-2 players like Tesla and Coreweave, which are deploying larger, more powerful server clusters. These clusters, featuring up to 200,000 GPUs, support next-generation AI workloads, including large language models with trillions of parameters. Hyperscale cloud providers are leading this trend, but enterprise adoption is accelerating, projected to account for 36% of industry sales ($23 billion) in 2025. Nvidia’s Blackwell GPU cycle is a major catalyst, with fully loaded server racks now valued between $3-4 million, up from $1.5-3 million during the Hopper cycle, highlighting the increasing complexity and value of AI server infrastructure.
Traditional server markets, growing at just 3% annually, pale in comparison to the AI-driven renaissance. This demand shift is reshaping the competitive landscape, with Dell, HPE, Lenovo, and EMS providers like Pegatron and Foxconn ramping up production. Liquid cooling capabilities and GPU allocation are becoming key differentiators as competition intensifies. While AI server margins remain below 20-22%, they are improving and are projected to reach the mid-teens in 2025 due to better GPU availability and evolving supplier dynamics. The regionalization of manufacturing to address trade concerns and security issues adds resilience to the AI supply chain, positioning it for sustained growth despite geopolitical uncertainties. This market transformation is creating opportunities for key players to secure larger market shares and drive profitability in this rapidly evolving space.
Our Valuation on SMCI is based on DCF Free Cash Flow to Firm
For the SMCI stock forecast, we adopted the free cash flow to firm DCF (discounted cash flow) approach, where we estimated 15.0% of WACC (weighted average cost of capital) and 5.0% of terminal growth rate. We anticipate revenue will grow at an average of 41.0% for the next five years and then gradually drop to 10.0% during 2030-40. According to our forecast, EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes) margins will reach 25.0%. For our assumptions, we have considered the recent trend of depreciation and amortization, capex, and net change in working capital. Based on our estimation, we value SMCI at $161 per share as of 2030.
SMCI is positioned to grow faster than the AI server market, which is projected to expand at a CAGR of 27.6% through 2033, due to its innovative and tailored approach. SMCI’s building block architecture allows for highly customizable server solutions, catering to specific AI workloads like training, inference, and data processing. This flexibility positions SMCI as the go-to provider for clients needing bespoke solutions, particularly in high-value niches.
The company’s proprietary liquid cooling technology further strengthens its appeal, addressing the energy-intensive demands of AI workloads with cost-effective and sustainable solutions. Holding a 23% share in the AI server market, SMCI is a recognized leader, benefiting from established partnerships with cloud providers, AI researchers, and enterprises. Lastly, SMCI is expanding into emerging markets like edge computing, 5G, and autonomous vehicles, which require its specialized infrastructure solutions.
SMCI’s Governance Troubles: Balancing Growth Potential with Governance Risks
Super Micro has shown remarkable growth and innovation, but its history of compliance and corporate governance issues poses significant risks to its long-term prospects. The company has faced delayed financial reporting, triggering concerns about internal controls and governance. Such delays erode investor confidence and invite regulatory scrutiny, as seen with the resignation of its previous auditor and ongoing Nasdaq compliance challenges. These issues culminated in SMCI’s removal from the Nasdaq 100, a development that not only harmed its reputation but also led to significant institutional selling, compounding its stock’s volatility.
Corporate governance concerns further exacerbate the risks. Investors remain wary of potential mismanagement, particularly given the complexities of operating in the fast-paced AI sector. While SMCI has taken steps to rebuild trust, such as appointing a new auditor and forming a special committee to address governance matters, the damage to its credibility has made investors cautious. In the short term, SMCI stock forecast remains heavily influenced by sentiment rather than fundamentals, with its valuation tied closely to the resolution of these governance challenges.
For SMCI to regain its footing, it must demonstrate consistent transparency, meet reporting deadlines, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. Failure to address these risks effectively could overshadow its operational successes and impede future growth. Conversely, if SMCI can overcome these obstacles, it could unlock significant upside potential, particularly given its strong market position and innovation in AI infrastructure. However, until the company can manage governance and compliance sustainably, it will remain under scrutiny, with its stock highly susceptible to negative sentiment and market volatility. Investors should approach cautiously, balancing the company’s growth potential against the persistent risks tied to its governance history.




